
By Muhammad Amir Malik
The concern most people share about the environment today is a relatively new phenomenon. The emergence of new environmentalism took place mostly in Western countries during the 1960s. The most crucial change in climate, which in turn triggers a number of other changes, is a warming of the biosphere (the parts of the earth’s surface, waters and atmosphere which support life). CO2, methane, ozone and other gases have increased markedly in the last 150 years. This change has been linked to human activities: economic growth, population growth, and changes in life-style. As ICTs have surfaced as the dominant means of human communication and a central source of globalization, their impact and role in the environment is starting to take center stage. As a growing, energy-intensive, ubiquitous industry, ICTs have a strong impact on the environment in virtually every country. Apart from being one of the sources of problem, ICTs can play a vital role in helping to facilitate research, analysis, awareness raising and cooperation to address critical environment issues.
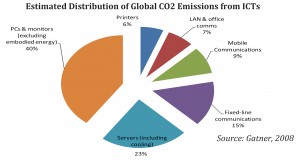 Global consultants Gartner estimate that ICTs presently account for approximately 0.86 metric gigaton of carbon emissions annually, or just about 2{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} of global carbon emissions. 1 The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has estimated the contribution of ICTs (excluding the broadcasting sector) to climate change at between 2{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} and 2.5{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} of total global carbon emissions. The main contributing sectors within the ICT industry include the energy requirements of PCs and monitors (40{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10}), data centers, which contribute a further 23{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} and fixed and mobile telecommunications that contribute 24{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} of the total emissions. According to calculations by consultants A.T. Kearney, worldwide IT now generates CO² emissions of about 600 million metric tons a year. And if the sector continues growing at the current rate, emissions in Germany alone are expected to increase by another 60{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} by the year 2020.
Global consultants Gartner estimate that ICTs presently account for approximately 0.86 metric gigaton of carbon emissions annually, or just about 2{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} of global carbon emissions. 1 The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has estimated the contribution of ICTs (excluding the broadcasting sector) to climate change at between 2{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} and 2.5{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} of total global carbon emissions. The main contributing sectors within the ICT industry include the energy requirements of PCs and monitors (40{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10}), data centers, which contribute a further 23{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} and fixed and mobile telecommunications that contribute 24{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} of the total emissions. According to calculations by consultants A.T. Kearney, worldwide IT now generates CO² emissions of about 600 million metric tons a year. And if the sector continues growing at the current rate, emissions in Germany alone are expected to increase by another 60{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} by the year 2020.
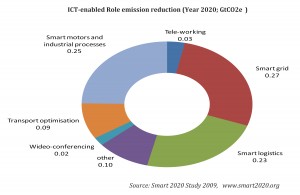
The Smart 2020 study estimates that approximately 7.8 GtCO2e emissions can be reduced by 2020 through proper ICT deployment; this is estimated to be 15{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} of emissions in 2020 (estimated at 51.9 GtCO2e) based on BAU (business as usual) estimates which would amount to approximately $946.5 billion in cost savings due to saved electricity and fuel consumption (smart grids). By the UN climate change panel IPCC: billion metric tons of CO2 equivalent is GtCO2e.
The methods of disposal, including incineration, of electronic waste (e waste) are another key environmental issue affecting climate change. Among the discarded artifacts are disused mobile phones, obsolete computer and television equipment, old cables and other ICT hardware. The ITU estimates that between 1996 and 2008 the number of mobile phones in use increased from 145 million to over four billion. Most of these will be discarded within one to three years of their life span. In many countries disused mobile phones, old computers and other electronic junk are discarded into existing general dump sites for domestic waste, where they are liable to be incinerated alongside other solid waste materials. The resulting carcinogenic emissions will add to the alchemy of harmful gases contributing to climate change. At the same time, the failure by manufacturers to maximize the life span of equipment increases the burden of emissions from the manufacturing sector.
Nevertheless, as ICT demand and utilization continues to expand, the net adverse impact of this sector on climate change and the environment in general is likely to increase steadily, unless strong measures are taken to alter the ICT energy equation. Some companies have taken leading steps, in cooperation with governments and environmental groups, to set examples of Green operating philosophies. One example is the web portal company Yahoo!, which announced in 2007 that it would implement ―carbon neutral practices in its operations. In 2010, Yahoo! announced plans for its new data center in New York, which was granted $9.9 million by the U.S. Department of Energy to implement energy-efficient plans, including use of wind and hydropower and specialized building design to increase natural cooling of the company‘s servers.
Improving environmental performance, tackling global warming and enhancing resource management are high on the list of global challenges that must be addressed urgently. The information and communications technology (ICT) industry needs to further improve its environmental performance (it is responsible for around 2-3{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10} of the global carbon footprint), and ICT applications have very large potential to enhance performance across the economy and society (the remaining 97-98{e1f18614b95d3cd6e4b3128e1cd15d99b042a60a5a19c19b7a8e07e7495efa10}). Governments and business associations have introduced a range of programs and initiatives on ICT and the environment to address environmental challenges, particularly global warming and energy use. Some government programs also contribute to national targets set in the Kyoto Protocol (e.g. Denmark’s Action Plan for Green IT and Japan’s Green IT Initiative). Business associations have mainly developed initiatives to reduce energy costs and to demonstrate corporate social responsibility.
 “Green ICT” is what analysts, manufacturers and providers call all ICT solutions that will save energy at business organizations. These include hardware, software and services. Where hardware is concerned, energy-efficient desktop PCs, thin-client architectures and data-center hardware offer answers, and so do energy supply and cooling systems. In the software and service area, it includes virtualization, dynamic capacity management, data-center planning, and in storage-system off-shoring. Green ICT also extends to other, less commonly considered aspects of the entire life cycle. This includes eco-friendly procurement, employee behavior, running data centers on sustainably generated energy, environmentally sound disposal of used electrical equipment, and as much recycling as possible. One has to clear that ICTs are not fundamentally “green”, because they consumes energy and raw materials. However, ICTs can be leveraged to make business processes more energy-efficient.
“Green ICT” is what analysts, manufacturers and providers call all ICT solutions that will save energy at business organizations. These include hardware, software and services. Where hardware is concerned, energy-efficient desktop PCs, thin-client architectures and data-center hardware offer answers, and so do energy supply and cooling systems. In the software and service area, it includes virtualization, dynamic capacity management, data-center planning, and in storage-system off-shoring. Green ICT also extends to other, less commonly considered aspects of the entire life cycle. This includes eco-friendly procurement, employee behavior, running data centers on sustainably generated energy, environmentally sound disposal of used electrical equipment, and as much recycling as possible. One has to clear that ICTs are not fundamentally “green”, because they consumes energy and raw materials. However, ICTs can be leveraged to make business processes more energy-efficient.
A vital action to direct actionable policies and funding could be the setting up of research centers to analyze effective and practical digital substitutions for socioeconomic development. They can be used to monitor and evaluate the balance between emissions output and reduction in a particular country environment.
March 10, 2026










