Over the last three years we have seen some of the major regional and global telecom operators, regulators and service providers work tirelessly to rapidly roll-out 5G commercially. While 5G technology is being leveraged by consumers to enjoy high speed downloads, faster internet browsing and experience lag free online mobile gaming, enterprises today have realized the capabilities of 5G to meet their industry’s growing digital transformation needs. This helps enterprise not only deploy use cases reliant on emerging technologies such as Industrial IoT, AI, Robotics and AR/VR but also unleash their true potential. One of the major reasons this has been possible is because of the ability of 5G technology that allows MNOs to create multiple 5G virtual networks over a shared physical network infrastructure that has already been deployed. A virtual 5G network service offered to an enterprise by using existing public 5G network is called as PNI-NPN (Public Network Integrated Non-Public Network) by 3GPP and can also be referred to as 5G Virtual Network. The logical and physical separation of virtual networks fuel digital transformation across industries as it helps meet many sector specific needs of security, privacy, bandwidth, and latency. Moreover adoption of MNO offered 5G Virtual Networks are more cost effective as compared to building a private wireless system which is capex heavy and requires additional investments in acquiring and setting up their own team of individuals with 5G network operation skills.
What are 5G Virtual Networks and why are they needed:
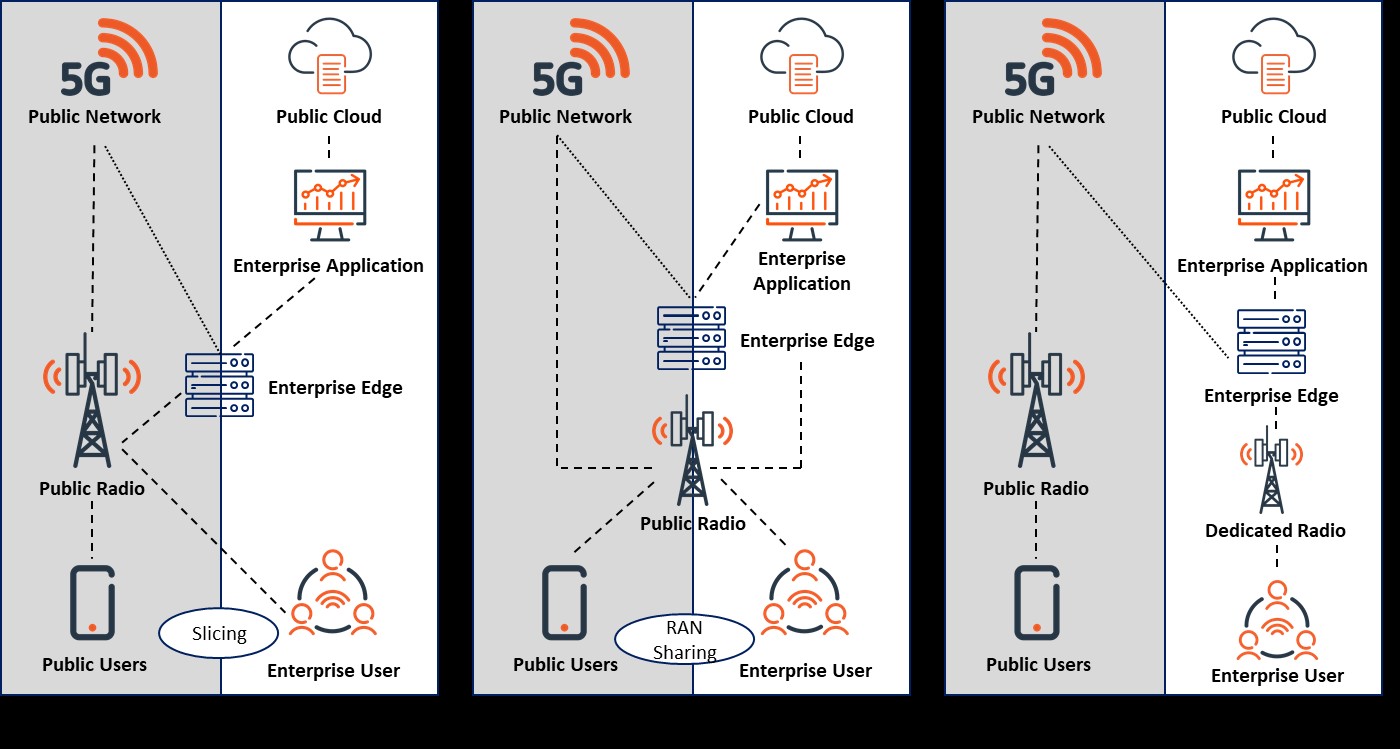
A 5G virtual network is an SLA backed dedicated 5G network service offered by MNOs to their enterprise customers. Leveraging the same 5G network and infrastructure deployed for consumers, MNOs create 5G Virtual Networks for enterprise customers which cannot be accessed by un-authorized users outside the enterprise. These 5G Virtual Networks have the capabilities to offer enterprise customers the required latency, bandwidth, and availability to cater to the use cases deployed within the enterprise while ensuring security and privacy. Organizations that have deployed Industry 4.0 use cases involving technologies such IoT, AI, Robotics, Drones etc. have hugely benefited from 5G Virtual Networks and hence we are seeing a growing number of industrial enterprises adopting 5G Virtual Networks to deploy use cases that can improve operational efficiency and help the business go to market faster with better services and products. Depending on the requirement and in some cases location of the organization, MNOs can deploy a few variations of virtual networks.
- Network Slice Deployment: In this deployment model MNOs leverage slicing concept introduced in 5G standardization to offer their enterprise customer a dedicated network slice that caters to particular use case or application. The network slice is dedicated to that enterprise and is logically separated from the public network but continues rely on the existing public network infrastructure and cannot be accessed by un-authorized users outside the enterprise nor does it interfere with other network slices. However, in this case the user plane functions can remain with the MNO or can be dedicated for an enterprise.
- RAN Sharing Deployment: In this hybrid deployment model the MNO creates a virtual private network using resources both dedicated and isolated. Although services are handled locally within the enterprise, the RAN is shared with the public network. The user plane functions for the virtual network lies with the enterprise which enables it to further create slices of their virtual network to be allocated to specific use cases or services. This deployment model has gained a lot of traction in recent times as it cost effective and offers licensed spectrum along with low predictable latency and high security.
- Dedicated Private Network: The 5G private network deployed using this model is completely isolated from the public network and is completely independent. The MNO in this case sets-up a completely dedicated infrastructure with the MNO’s licensed spectrum for an enterprise. The network is managed by the enterprise or in some cases even the MNO. However setting up such a dedicated private network involve high capex and a highly skilled IT team
The capabilities of 5G virtual networks to deliver high transmit speeds – faster than 4G LTE and Ultra reliable low latency (uRLLC), highly available networks capable of supporting large volume of devices and IoT sensors – paves the way for organizations to deploy complex technologies such as AI driven applications that cater to large amount of sensors and endpoints. Similarly, it can enable machine learning algorithms to be applied on massive amounts of data that can be processed locally using distributed cloud architectures and edge computing, without leaving the security and privacy of the network, thus considerably reducing cybersecurity threats by controlling exposure to public networks.
Key factors driving the adoption of 5G Virtual Networks:
Building operational efficiency: As organizations embark on their digital transformation journey, real time data driven analytics to create efficient services and offerings will take center stage. This would require adoption of new and emerging technologies such AI, robotics, machine learning and edge computing – where 5G will play a pivotal role.
Industry 4.0 driven IT & OT convergence: As more industries start deploying Industry 4.0 uses cases the convergence of IT and OT will be a key consideration. This will lead to the need for high-bandwidth, low-latency networks to support increased automation requirements.
Data security and privacy: Security of data and applications continues to remain the top priority for IT leaders. The flexibility and control offered by 5G virtual networks to make critical assets unreachable will act as a major driver.
Need to replace networks nearing end of life cycle: In case of mission critical networks which predominantly work on narrowband networks and are very critical for public safety are nearing end of life cycle and hence need to be replaced by cellular technologies which are much more efficient.
Although public 5G networks which have been commercially rolled out are considerably capable, however the flexibility, ease of operation along with key features such as dedicated high bandwidth and ultra-low latency of virtual private 5G networks will fuel digital transformation and shape industries of the future.
What do 5G Virtual Networks Offer– Key Characteristics and Advantages
State of the art manufacturing sites, oil & gas processing plants, healthcare facilities, utilities along with many other verticals can leverage the deployment of 5G virtual networks. Operational efficiency can be achieved from algorithmic updates to a production processes, predictive maintenance of machinery and real-time interaction with autonomous distribution vehicles, all with the help of 5G virtual networks. The ability of virtual 5G networks to deliver a secure network with high availability and reliability ensures that critical civil functions and business processes have access to high-quality communication, even when parts of the system fail due to any external factors. In addition, one of the key aspects of 5G Service Based Architecture (SBA) is the capability to create distinct network slices. This enables MNOs to split their public network creating a practically unlimited number of private virtual 5G instances supporting their enterprise customer. Additionally, an enterprise customer can have their allocated 5G virtual networks further split – to allocate it to various services and process based on bandwidth and latency requirement.
5G technology and standards have been developed keeping in mind the requirements of digital transformation enabling technologies. The 3GPP within its several releases has defined these capabilities as ready to cater to the digital transformation requirement of several industries. In Release 15 (R15) and R16, the capabilities for both Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) and Ultra Reliable Low Latency Connection (uRLLC) have been articulated. It has been affirmed that 5G can deliver ultra-low latency connection and vertical slicing requirements for several industries. The R17 release which been finalized and set for March 2022, defines Massive Machine Type Connection (mMTC) capabilities that support more enhanced vertical industry use cases with additional slicing functions.
Key technical features of 5G:
5G Air interface and MIMO: 5G Air interface and use of large-scale Massive Multi-input Multi-output (MIMO) antenna technology greatly increase the peak and average cell throughput, enhances resolution and improves signal power while significantly reducing multiuser interference. 5G uses F-OFDM as the air interface waveform, further improves flexibility and spectrum utilization efficiency, and is a basic technology for 5G air interface slicing, which meets the requirements of ultra-large bandwidth, ultra-low latency, and ultra-large-scale connection.
Reducing Delay: 5G is designed to reduce delay. 5G uses LDPC code as the coding scheme for 5G data channels, which has advantages in decoding capability, decoding delay, chip size, and power consumption. Polar code is used as the coding scheme for the 5G control channel, which is closer to Shannon limit curve.
Lowering latency with flexible frame structure: 5G flexible frame structure design can lower latency, 5G introduces flexible frame structure design through configuration of multiple parameters such as uplink-downlink ratio configuration, subcarrier bandwidth, and system bandwidth, uplink grant-free, mini-slot, etc. With the edge user plane function and new network architecture, 5G will effectively meets the 1ms user-plane latency requirement of the International Telecommunication Union.
Massive connectivity: 5G Multiplex methods provide massive connectivity. In 5G, Narrowband Internet of Thing (NB-IoT) can use OFDMA in the downlink, and SC-FDMA in the uplink. Therefore significantly increase the number of devices per site. i.e., the number of NB-IoT connections per 5G site can reach 100,000, and the number of eMTC connections per site can be set to 50,000.
Integrated mobility and handover mechanisms: 5G mobility and handover mechanisms improve performance. In 5G, the mobility and relevant handover mechanisms are fully integrated between the network and user equipment, which minimalize handover processes and provide more stable data transmission compared to the WIFI technology. With minimal delay and smooth handover, 5G is a more suitable technology for managing the industry use cases such as remote control, mobile video transmission, and AGV.
Network Slicing: 5G ‘slicing’ can ensure network isolation and ability to provide Service Level Agreement (SLA) Assurance and security that is required in a private or dedicated network using shared network infrastructure. With slicing each service user could define the network resources physically or logically isolated from others, with specific instances of the 5G network dedicated to users and services as per their exact and specific requirements, security, and SLA. Additionally, ‘slicing’ allows the logical separation of access, control and forwarding in 5G architecture, which can avoid a large number of devices failing to access the network due to radio resource conflicts during initial process of accessing the network.
Delivering uRLLC with Multi-access Edge Computing: 5G supports the use of Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) which can ensure industry needs for ultra-reliable low latency and high throughput needs. 5G allows for the most agile possible deployment of the network to meet every possible use case in the ultra-reliable low latency, high throughput communication. MEC allows for edge to be more reliable and robust, 99.999% reliability is foundation of 5G networks and with MEC we can bring telco grade reliability to the enterprise world. In addition, the MEC can meet the requirements of enterprises’ network while keeping enterprise data inside their campus.
High security resilience: 5G architecture design is highly secure. In addition to more robust encryption method which is used in 5G with concealed IMSI using SUCI/SUPI concept, 5G network can provide better integrity check on both user plane and control plane messages. It guarantees better security resilience, privacy & identity management, and communications security across 5G radio, transport, and core network.
How are 5G Virtual Networks accelerating digital transformation across industries
As market evolves, consumer demands have also matured and grown. To keep up with the continuously evolving market dynamics and competition, organizations need to constantly change their approach to adapt to the changing market conditions. This shift in the market dynamics has pushed several organization to rethink their approach and embrace digital transformation to deliver unique customer experiences while making their processes streamlined, cost effective and secure. Digital transformation has been a top agenda for many businesses across all industries. However to embark on the digital transformation journey organizations need to adopt and unleash the potential of several emerging technologies such as analytics and automations that help in structuring and understanding data in an insightful manner to make critical business decisions, drive operational excellence, and cost savings. In the backdrop of digital transformation and deploying Industry 4.0 concepts, the importance of 5G virtual networks cannot be understated.
In the past emerging technologies like IoT, AI, VR, predictive maintenance has conceptually shown tremendous potential, however it has been difficult to deploy these technologies and harness their complete benefit. With the introduction of 5G and 5G virtual networks, unleashing the true potential of these technologies has become a reality. Today we are seeing industry leaders leveraging virtual 5G networks to build smart factories by enabling everything from IoT sensors to robots which are generating a plethora of data that unlocks the next levels of inventory tracking, safety, sustainability, and productivity. Similar transformational trends such as robotic surgery, autonomous cars to drone delivery are being observed within all verticals including public sector, healthcare, retail etc. Achieving this would not have been possible without 5G virtual networks which has truly unleashed the next generation of transformation.
Digital Transformation in Manufacturing sector – an early adopter of 5G virtual networks
The manufacturing vertical has been among the early adopters of 5G virtual networks. Manufacturers have deployed 5G virtual networks in factories to support mobile assets such AGVs, as well as applications that drive productivity gains, health, and safety, such as video surveillance. In China, Media Group – one of the largest home appliances manufacturing company has adopted a 5G virtual network with the help of solution partners Huawei and China telecom. Media Group has established 11 application scenarios and 1 laboratory and is leveraging 5G to operate services such as data collection, modeling and data feedback. This has helped significantly improve production efficiency. The organization has worked out the application of Industrial Internet + 5G + AI in various fields including production safety, flexible manufacturing, and smart logistics, which has effectively reduced the costs of production and maintenance and the cost of production line self-inspection. Ultimately, this has helped in increasing the overall operation and maintenance efficiency by 17% and decreased the costs by 10%.
With 5G enabled technologies such as collaborative mobile robots, self-driving machines, Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs), augmented reality (AR) predictive maintenance, AR/VR headsets, digital twins etc., at the foundation of smart factories – 5G virtual networks offer remarkable benefits to manufacturers. Manufacturing industry leaders are heavily relying on 5G virtual networks to future-proof their plants to remain competitive and drive operation excellence. The success from the manufacturing sector will soon resonate amongst all sectors and will push them to follow a similar path towards digitally transforming their business.
Although the hype surrounding 5G centers on its ability to deliver superior consumer experience through faster speeds for consumer applications. However, while building a digital transformation and a consolidated network strategy CIOs and IT leaders should take into consideration the potential of 5G Virtual Network which can equip organizations with improved customization abilities and full control of their own connectivity while delivering higher speeds, lower latency and robust reliability as compared to existing commercial services like 4G LTE or other network infrastructure.











