5G is the latest generation of mobile communications technology. But what, exactly, does 5G offer and why should you care?
Whilst consumers are focused on download speeds and looking for the ‘killer app’, industry meanwhile is seeing innovative changes that will change the way the world works, quite literally, and not many people are aware of this.
In this story, we will highlight how the lightning fast speeds of 5G, combined with the vast numbers of connections are not only just facilitating faster downloads, but this is enabling industry to automate complicated and often dangerous tasks. Huawei’s 5G connectivity, when combined with cloud, and artificial intelligence (AI) is allowing humans to control machinery in mines, ports and factory floors remotely vastly improving energy efficiency and driving productivity across industries like manufacturing, energy, and transportation.
While digitalization creates business value by delivering productivity gains, it also provides significant social value by enabling safer and more hospitable working environments.
We will finish up by looking ahead to the next generation of communications, 5.5G. This will enable speeds and connections at ten times the rate we have today, ushering in the AR, VR and autonomous driving solutions that will be the drivers of the digital economy.
I have included a document with supporting facts and case studies.
What is 5G?
5G is the latest generation of mobile connectivity technology that offers much faster speeds, virtually unlimited connectivity and lower latency (the time it takes a signal to travel from point A – point B)
5G is a relatively new technology that enables vast amounts of data to travel faster than ever, by using higher frequency radio waves on new frequency bands allowing our phones to connect swiftly no matter where in the world you are.
Why should you care?
The result is ultra-reliable connectivity to billions of devices with near zero waiting time whilst using 10x less energy per bit of data than 4G.
5G will see the realization of consumer use cases in future applications of VR and AR. This is already apparent in map software which uses the phone camera to confirm your location and provide heads up direction displays.
“There are perhaps more obvious advantages with 5G Fixed Wireless Access, which delivers a viable high-speed broadband experience for homes and businesses, either where the available wireline options offer poor performance or are expensive compared to a combined smartphone and broadband package from your 5G operator.”
Phil Kendall, Executive Director, Service Provider Group at analyst firm TechInsights
The Business case for 5G
According to the World Economic Forum, the influence of digital transformation on industries could be worth as much as US$100 trillion over the next decade. These scenarios have high requirements on latency (ultra-low, down to microseconds), reliability, security, and green, low-carbon development.
Digital and intelligent technologies enable industry to automate processes and boost economic growth. They create business value by delivering the next generation of industrial productivity, while also providing significant social value by enabling safer and more hospitable working environments. Technological innovation drives industrial digitalization and creates both business value and social value
5G has powerful enterprise use cases that are already supporting industry 4.0 objectives, it is the technology catalyst that is changing everything for industry. In agriculture, for example, 5G connections allow tractors and other farm equipment to move across fields almost autonomously. Precise routing of a tractor’s path can reduce fuel consumption by 17%, while intelligent sensors that distinguish weeds from other plants can reduce pesticide use.
In shipping and port management, cameras equipped with machine vision can identify serial numbers on shipping containers and inspect them for damage. The high-definition video is transmitted on a 5G network that also allows cranes to be operated remotely. This makes unloading containers more efficient, while sparing operators the long-term health effects of sitting in a cramped cabin 40 meters high and looking down all day, a posture that can cause chronic neck and back pain.
In manufacturing, 5G’s high throughput (the amount of data transmitted per second) will speed up transmission of data collected from industrial machinery, allowing better decisions to be made more quickly. 5G-connected robots are already being used to optimize the movement of heavy loads across factory floors. In fact, a 2021 survey showed that 91% of manufacturers believe 5G connectivity will be important for their business in the future.
The auto industry will also rely heavily on 5G’s capabilities. Connected cars will be able to communicate with each other, transmitting information about road conditions wirelessly and in real time. Fast 5G connections will also allow real-time monitoring of the car’s critical systems, which will improve performance and efficiency. Passengers will be able to watch high-definition streaming video with little or no delay, making long car trips easier for parents and kids alike.
5G industry applications have entered a golden period. 5G has been successfully deployed across 50% of 97 major industries, including manufacturing, mining, steel, port, chemical, cement, power grid, and healthcare. The total number of 5G use cases across industries has exceeded 20,000, and the service revenue of carriers’ 5G private networks has increased by more than 100% year on year. 5G has now been in large-scale commercial use worldwide for more than three years. Carrier 5G services have become a new engine of growth for Huawei and a range of businesses and industries
Huawei has signed more than 5,000 5G/F5G digital project contracts with carriers and partners in more than 20 industries. Huawei’s industrial 5G solutions have been replicated at scale in numerous typical application scenarios.
Huge numbers of interconnected machines, all exchanging vast amounts of data in real time allow for new insights into business processes and operations. Connecting everything in the physical world to the digital world allows data to be measured and analysed. Huawei’s application of AI onto high-quality data transforms information into knowledge which facilitates smart action across multiple industries
Smart manufacturing
Manufacturing is an excellent working example of how 5G is driving digital transformation. Smart factories have automated production lines and use AI to optimise production processes. 5G enables sensors on equipment to feedback data and allow autonomous assembly lines that are efficient, flexible and cost effective.
Healthcare
With the use of 5G, doctors and other healthcare professionals can provide remote consultations and virtual appointments with patients in rural areas. Medical records can be easily accessed from anywhere and scans and other medical data can be uploaded quickly from remote areas. When this is combined with AI to interpret diagnostics of medical records and scans, x-rays etc it can aid the diagnosis for doctors in record times.
So, if 5G is so good, what is 5.5G for?
5G is offering ubiquitous upload speeds of 1Gbps and low latency, 5.5G is planning on doing all that 10x faster and more efficiently.
The 5.5G era will help carriers extend into five new business frontiers and provide carriers with a 100-fold increase in new business opportunities.
- 10 times higher speeds: The peak rates experienced by mobile and home broadband users will increase from 1 Gbit/s to 10 Gbit/s, ensuring better experiences in immersive and interactive services.
- 10 times more connections: Passive IoT technology enables an increase in the number of connected things from 10 billion to 100 billion.
- 10 times as much certainty: There will be a 10-fold improvement in latency, positioning accuracy, and reliability.
- 10 times higher energy efficiency: CO2 emissions per terabyte of data transmitted on a mobile network will be reduced by 10 times.
- 10 times as much intelligence: Autonomous driving networks (ADN) will be upgraded from Level-3 to Level-4 autonomy, with 10 times more efficient network O&M.
Huawei’s evolution towards 5.5G and beyond will to bring more advanced capabilities, higher speeds and greater connectivity to support the growing number of connected devices and emerging applications for the smart connected digital world.
5G – The technology
- Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology uses large antenna arrays to transmit and receive huge amounts of data simultaneously. This increases network capacity, meaning more devices can be connected in a given area.
- Beamforming technology focuses wireless signals directly at a specific device or location. This helps increase network efficiency and reduces interference. Millimetre wave allows faster data transfer rates and lower latency, albeit over a shorter distance.
- Network slicing facilitates multiple individual virtual networks within a larger network. Each virtual network can be optimized for a specific use case, enabling businesses to tailor their network to their specific needs.
- Edge computing allows data to be processed close to source, instead of transmitting it to a centralized data centre. This improves the performance of applications that require real-time data processing such as automated factories.
Supporting data
Huawei has served more than 2,800 medical institutions and 50 of the top 100 financial institutions. We have forged in-depth partnerships with nearly 200 power enterprises worldwide and provided digital services for more than 20 leading oil and gas enterprises and 800 mining enterprises. In addition, we serve more than 100 airports and 100 ports, and have helped customers upgrade more than 200,000 km of roads, 300 urban rail tracks, and 150,000 km of railway tracks.
Driving development: the impact of ICT investments on the digital economy
- A 10% increase in mobile adoption can result in a GDP increase of 1%
- 5G alone is expected to result in additional global GDP value-add of US$960 billion, or about 0.7% of global GDP
- the effect increases by approximately 15% when connections were upgraded from one mobile network technology to another (from 2G to 3G and from 3G to 4G)
ICT infrastructure and industry digitalization that it enables are set to drive the fourth industrial revolution, similar to how steam power and mechanization drove the first industrial revolution three centuries ago
Telcos have a pivotal role to play as enablers of the digital economy. They have been instrumental in providing necessary connectivity infrastructure and improvements in connectivity.
Advanced 5G connectivity is the undercurrent enabling technology adoption and its benefits. There is a sharp focus on technology adoption and implementation, such as the greater use of AI, machine learning, and cloud and edge computing. However, the base requirement for all of this is the availability of and advancements in high-speed, reliable 5G network connectivity to 5.5G and eventually 6G. Without investment in networks, the gains from technological developments will be stunted.
Investment in ICT unlocks value for the planet and communities. New and emerging ICT technologies are proving to be instrumental in energy use management, reduction in carbon emissions, in improvements in SDG benchmarks and contributing to community resilience. Traditional Investment in ICT mainly focuses on connectivity and computing. Green technologies will be the third new dimension to maintain long-term vitality of the whole digital economy, improving sustainability and resilience, while unlocking value for communities and the planet.
Case Studies
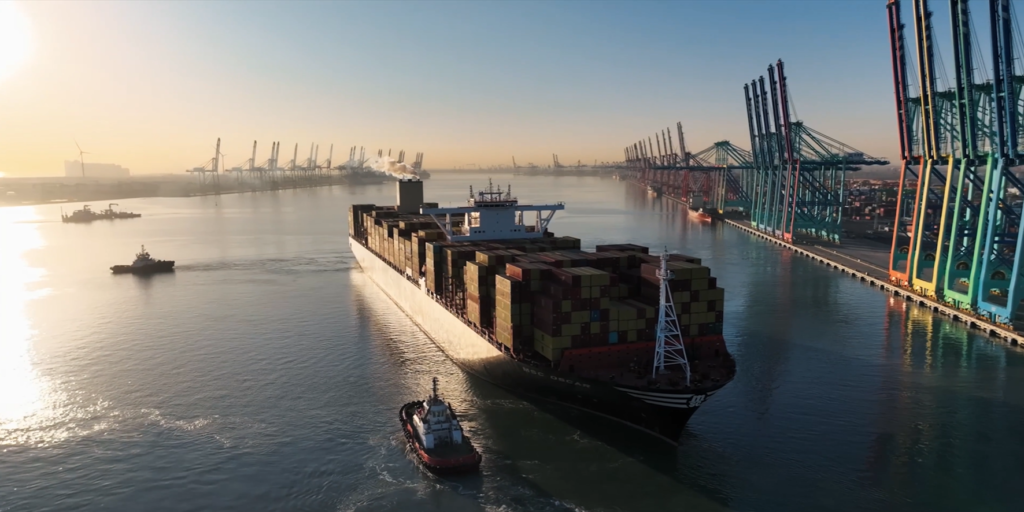
Case Study 1: Port of Tianjin: The world’s first smart, zero-carbon container terminal
A more efficient, yet safer port where 5G-connected trucks circulate driverless
You can barely see any workers at the intelligent Section C Terminal of the Beijiang Zone of Port of Tianjin. There, container cranes operate automatically and unmanned electric container trucks come and go at high frequency. Remotely controlled quay cranes lift loaded containers from cargo ships and put them onto unmanned vehicles. Supported by China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, the trucks are guided to automated workstations. They then go on to the container yard along optimal driving routes that are calculated in real time. The entire process runs smoothly.
This terminal is the latest result of a collaboration between Tianjin Port Group, Huawei, and numerous other partners, all of whom are working together to create a world-class, smart, and green port. Section C Terminal commenced smart operations in October 2021, and has been stably operating ever since. One of the key innovations applied is a true AI-powered intelligent horizontal transportation management system. Section C is the site of the world’s first large-scale commercial deployment of Level 4 autonomous driving in ports, the world’s first “5G + BeiDou” integration, and the world’s first port to achieve self-sufficiency in wind electricity, meaning the port’s end-to-end operations produce net-zero carbon emissions.

Learn more: https://www.huawei.com/en/media-center/Multimedia/videos/2023/Tianjin-smart-port
Case Study 2. Digital Technologies Help Mines Safe and Efficient
Smart Coal Mine: Shaanxi Hongliulin Mining Industry
Dusty, hazardous, and yet essential. Mining is an indispensable industry that has been chronically unpleasant. Until now. But this is about to change.
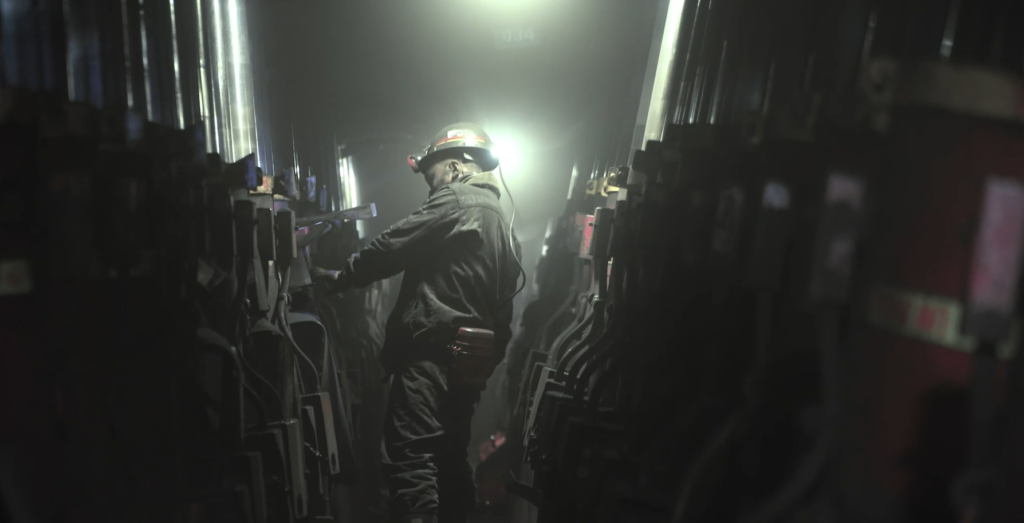

In China, Huawei has been working with partners to create integrated smart mining solutions at both open-pit and underground mines. The results are dramatic. At open-pit mines, remotely-located operators can man up to four driverless trucks to ferry the ore from the excavator to the processing facility for crushing and processing. As for the excavators, they are also remote-controlled. Fewer miners in the pit means fewer chances of mining deaths or injuries.
Huawei’s 5G smart mining solutions can be deployed deep under the ground as well as in open pit mines. This will help the industry to become safer and more efficient, while requiring fewer people for undesirable and dangerous assignments.
Learn more: https://www.huawei.com/en/media-center/our-value/Huawei-transforms-coal-mining-in-China
Case Study 3. Jingzhou, China: Midea builds first all-5G connected factory
Full 5G connectivity enables greener, more efficient production
Midea Group is a leading electrical appliance manufacturer in China that is rapidly becoming a pioneer in 5G-powered manufacturing. With advanced mobile solutions provided by China Mobile and Huawei, Midea has built the world’s first fully 5G-connected electrical appliance factory in Jingzhou, China. It marks the first time 5G has been fully applied to all industrial production and business operations in a factory. In this smart factory, 5G is deployed across 15 scenarios and all production links are seamlessly connected through 5G. The project has seen 5G replace complex cabling between machines in the factory, allowing machines to operate automatically for higher productivity. The distributed Massive MIMO technology enabled by 5G also delivers a deterministic uplink capacity of over 1 Gbit/s per 1,000 m2, helping improve AI quality inspection efficiency and increasing defect detection rates by 10%.
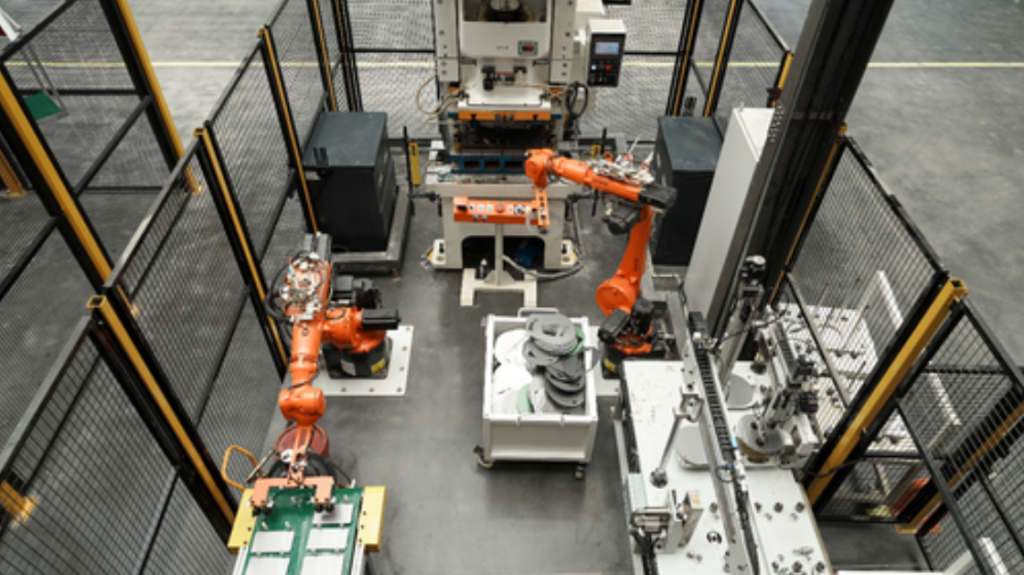
The benefits from the project are tangible: it now takes just 15 seconds for the production line to produce a single washing machine, and the number of products delivered directly to customers after coming off the production line has doubled. This slashes warehouse inventory by 50% and reduces by 30% labor costs required to produce a machine, allowing Midea to improve both quality and cost effectiveness, while also moving towards greener and safer production.
Moving forward, Midea will continue to work with partners like China Mobile and Huawei to keep innovating and accelerate its digital transformation of factories with 5G and other technologies.
Learn more: https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2023/2/mwc2023-5g-fully-connected
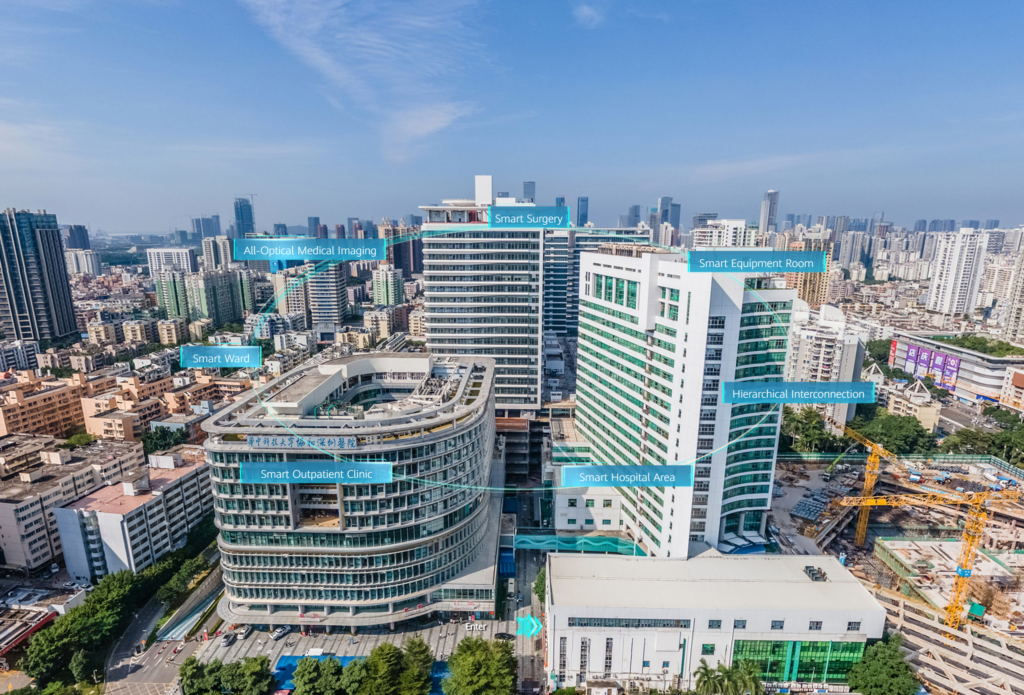
Case Study 4. Shenzhen, China: A smart hospital powered by Huawei Campus OptiX
Building a high-quality smart hospital with all-optical networks
As hospitals go digital faster, telemedicine, teleconsultation, and Internet-based diagnostics and treatment services are becoming increasingly popular. All these changes are being driven by the evolution of information infrastructure and particularly the evolution to F5G. F5G is the fifth generation of fixed networks that provides high bandwidth, low latency, and all-optical connections over fiber networks. Compared with traditional networks, F5G makes deployment and operations and maintenance (O&M) easier, delivers better network performance, and enables faster data transmission.
One hospital in the Nanshan district of the city of Shenzhen has deployed Huawei’s Campus OptiX Solution. With a simplified architecture, it provides fiber connections that help build the hospital’s Internet of Things (IoT). This solution has enabled high-quality information sharing in diagnostics and treatment rooms, wards, and CT scanning scenarios. After the all-optical network architecture was deployed, data access has become smoother than ever. Take medical imaging for example. About 1,000 images are generated during a dual-source CT scan. It might take 20 to 30 seconds to access this group of data during service peak hours over a traditional network, but with the new all-optical network architecture, reading such data only takes one second.
This solution has also facilitated referrals between this district-level hospital and community health centers, as it allows for teleconsultation and quicker sharing and access of test results. This helps make full use of the hospital’s high-quality medical resources, promotes equity in healthcare, and brings more convenient and quality healthcare services to the general public.

Learn more: https://e.huawei.com/en/case-studies/enterprise-transmission-access/2021/campus-optix-xiehe-hospital
Case Study 5. Germany: Volucap uploads gigabits of 3D video data in seconds
Enabling media startups to innovate and develop
Volucap is the first startup in Europe to shoot VR/AR images with wrap-around lens arrays. Their innovative wrap-around lens arrays typically contain 30 to 150 industrial lenses, so they can obtain holographic videos that can be played back and edited at any angle. The images captured can be used for VR video, gaming, and high-quality event broadcasts. Both shooting and processing have high requirements for networks, storage, and computing power because of the large amounts of data that need to be transmitted and processed. “The data of all the books in the world is equal to only five minutes of volumetric capture with our current system,” according to an employee from Volucap.



With Huawei Cloud, Volucap achieved an average data upload rate of 13 Gbit/s which enabled the company to transfer a half-day shoot transfer in two hours. This is possible thanks to Huawei Cloud’s strong presence in Europe. Huawei Cloud has set up R&D innovation centers, O&M centers, and partner cloud support centers in countries like France, Germany, Ireland, and Hungary to better serve its customers in Europe. Through these centers, Huawei aims to develop the best possible products and solutions for the European market and help develop local ecosystems and startups across the continent.
Learn more: https://www.huawei.com/en/media-center/our-value/Volucap











